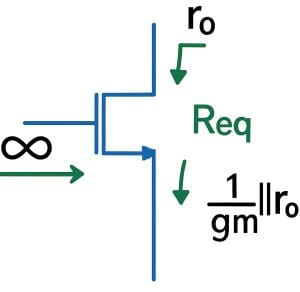
A MOSFET device exhibits different impedance characteristic when viewed from each of the 3 main terminals.
In summary, the MOSFET presents a high impedance node when looking from the Drain and a low impedance node when viewed from the source.
The impedances seen from the terminal of the transistor can be approximated as follows:
Contents
Gate Terminal Impedance
The equivalent resistance looking from the gate is considered infinite at low frequencies. At high frequency, the capacitances Cgs and Cgd come into a play, reducing the impedance as a function of frequency.
Drain Terminal Impedance
The impedance seen from the Drain terminal is considered high (in comparison with the Source impedance). It can be calculated by injecting a current (ix) from a voltage source (Vx) to the drain node.
Using the complete small-signal model, the circuit can be depicted as:
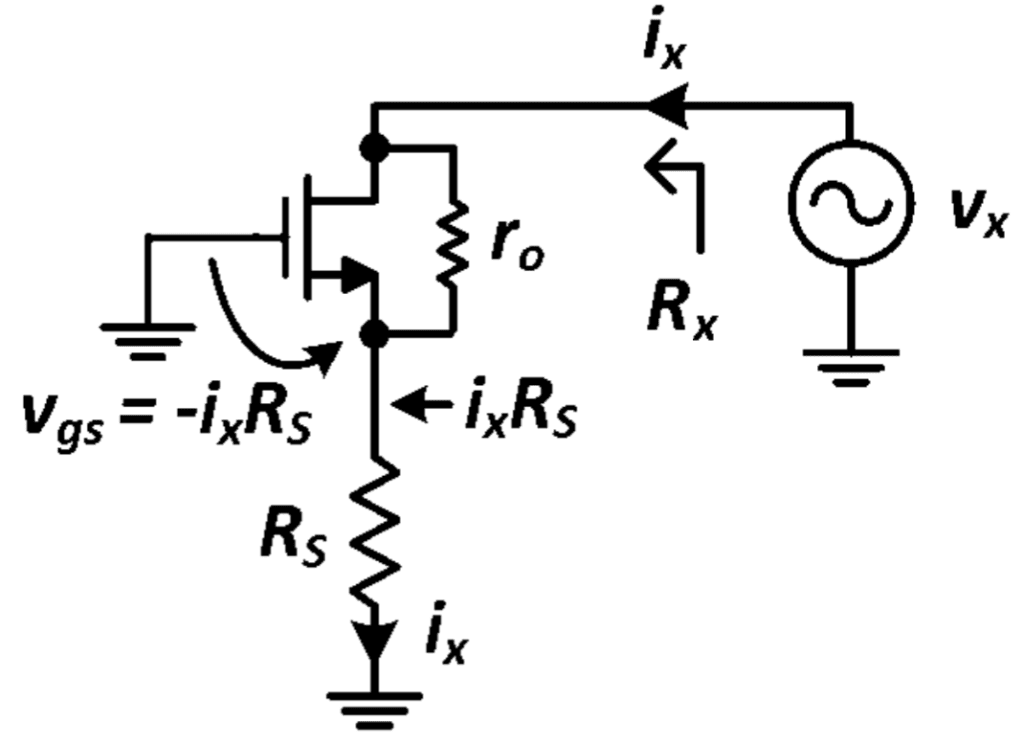
Where Rs is any resistance attached to the source.
Applying the KCL (Kirchhoff’s Current Law) at the upper node:
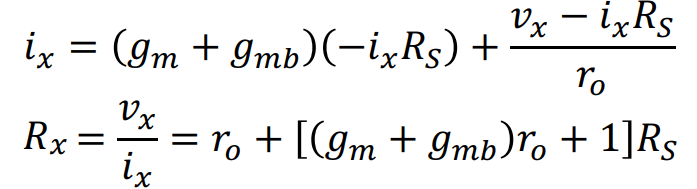
Note that if the source series resistance is zero (Rs = 0), the resistance is only Rx = ro.
Source Terminal Impedance
The equivalent impedance viewed from the source terminal is considered low impedance.
Let’s calculate the impedance using the same method as before.
The equivalent circuit is:
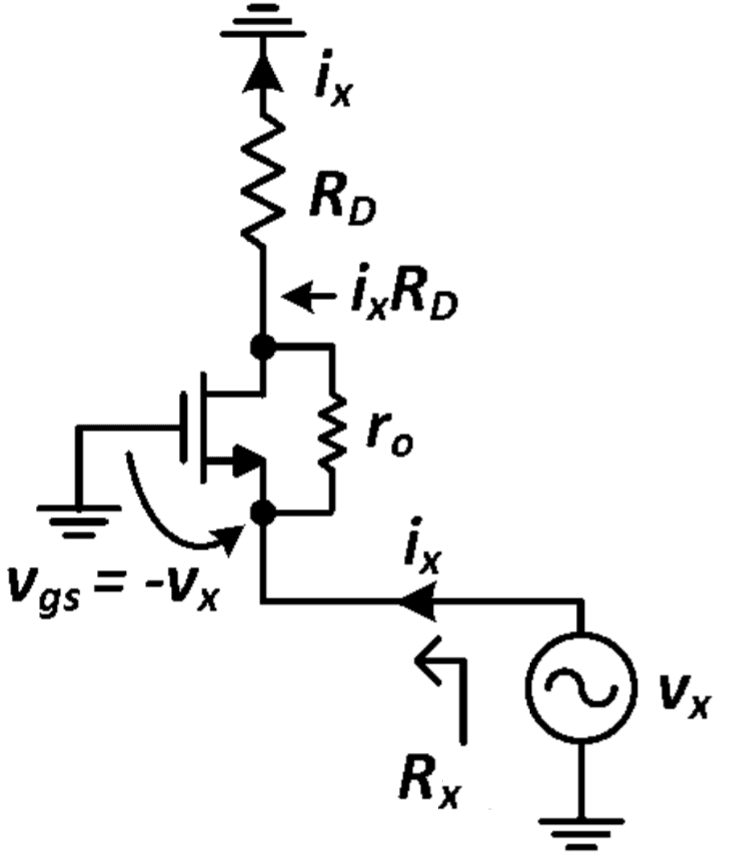
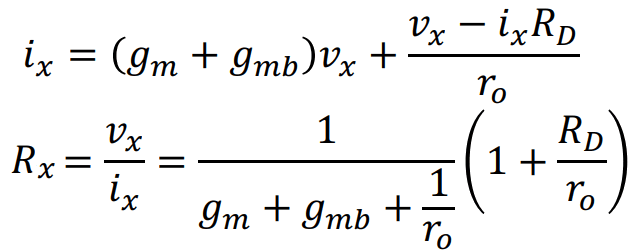
For the special case where the drain series resistance is zero (Rd=0), the input resistance seen from the source is 1/(gm+gmb), which is equivalent to a diode-connected transistor. Neglecting the body effect, the source resistance can be approximated as 1/gm.
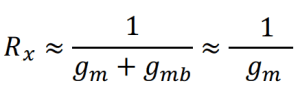
Moreover, the resistance seen from the source can be approximated to 1/gm if the Rd is much smaller than ro (Rd << ro).
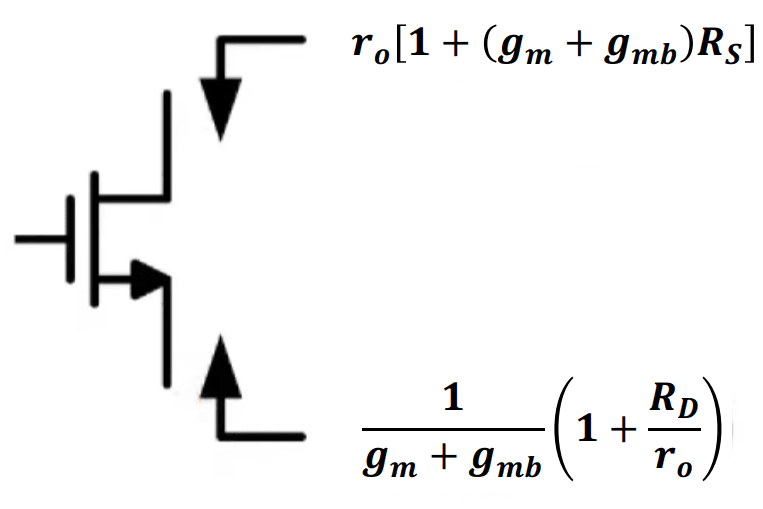
Impedance Seen from each Node of the MOSFET
In summary, the impedances seen from the drain and source terminals can be expressed more accurately as:
The output resistance of a MOSFET (ro, called “R-knot”) can be expressed as:
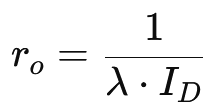
It is derived from the output conductance (go) for the device operating in the saturation region.
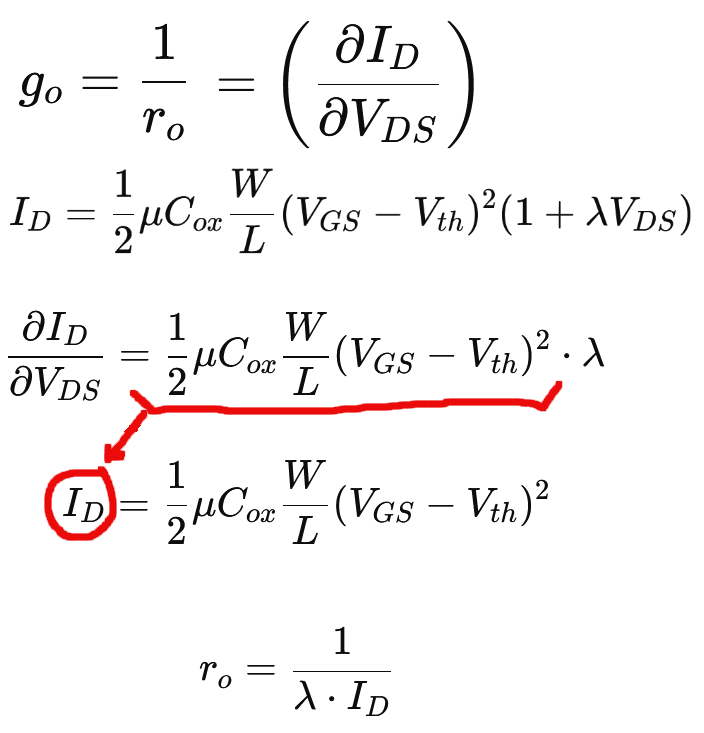
Understanding the impedance characteristics of MOSFET terminals is essential for analyzing and designing IC circuits.
Recognizing by inspection the high or low impedance nature of the drain and source aids in small-signal analysis, predicting the circuit behavior.




