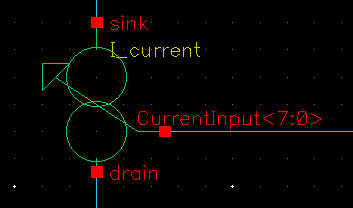
A binary-to-thermometer decoder digital block is created in Cadence. The VHDL code example transforms an 8-bit vector into 256 thermometer signals.
Thermometer Code
[Cuadro texto=’The thermometer code converts an N-bit number into a series of ones followed by zeroes of size 2^n’]
The thermometer code, also referred to unary code, is useful to transform the input vector and use it to drive several switches, as I show in this example of a digitally controlled current source. Also, it is used to perform smoother transition during the most significant bit changes, instead of the binary-code.
Example Code
In this example, an 8-bit vector is going to be transformed into a 256 output vector (thermometer-encoded).
The thermometer coder block is written in VHDL, but it could be extrapolated to Verilog:
--Libraries declaration
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
use ieee.numeric_std.all;
use ieee.std_logic_arith.all;
use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all;
entity thermometer is
port
(
vector_in : in std_logic_vector(7 downto 0);
vector_out : out std_logic_vector(255 downto 0)
);
end entity;
architecture vhdlams of thermometer is
signal salida : std_logic_vector(255 downto 0) := (others => '0');
begin
process(vector_in)
variable intermediate: integer range 0 to 255;
begin
intermediate := CONV_INTEGER((vector_in));
salida <= (others => '0');
for i in 0 to intermediate loop
salida(i) <= '1';
end loop;
vector_out <= salida;
end process;
end vhdlams;Test Bench
The Verilog block was simulated in Cadence. For the test bench, an 8-bit counter signal is given as an input vector to the block under test.

The output waveform: